Department of Engineering Geology and Geomechanics
Our Department main scientific focus is geotechnical assessment of a subsoil for determining engineering geological conditions based on field and laboratory tests, and assessment of soil and rock units for engineering purposes. It encompass using geological-engineering assessment as a tool for designing optimal solutions for spatial planning and urban development, or to help to improve unfavourable geological engineering conditions, e.g.
Particular research topics, areas and tools might be summarized as follows:
- behaviour of natural and anthropogenic soils under static and dynamic loadings;
- geospatial data analysis for evaluation of geological and environmental conditions;
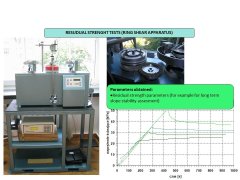
- slope stability assessment including creep;
- settlement analysis of a subsoil induced by groundwater drainage;
- determination of insulation characteristics of clays as geological barriers in landfill’s designing;
- prognosis of physical-mechanical properties of soils on the basis of their structure;
- prognosis of quantitative changes of geological environment as a result of: landslides, suffusion, liquefaction, long-lasting filtration, sedimentation in river valleys, wastes storage;
- prognosis of long-term geological-engineering conditions changes;
- geotechnical assessment of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils, including analysis of changes in physical and mechanical parameters due to contamination in comparison with natural soils, including analysis of microstructure of natural and contaminated soils
- design methodology for rock engineering;
- in situ and laboratory testing of rock properties for petroleum industry, urban planning, open cast and underground mining, tectonic studies and assessment of rock resources;
- non-destructive and destructive testing of rock elasticity properties;
- specific and regional geomechanical characterization of rocks and rock massifs;
- acoustic emission measurements;
- fracture toughness testing;
- structural geometry of rock and rock massif;
- state of stress as a component of rock pre-failure and post-failure path of deformation;
- mechanism of rock structure damage in relation to lithology and diagenesis factors;
- regional data collection and gathering rock properties;
- rocks as a sustainable material – zero-waste use of rocks;
- deterioration of rock material under different environmental factors, e.g. air pollution, salt action, sun action, freeze-thaw action.